IBM Security announced the results of a global study examining the financial impact of data breaches, revealing that these cost companies an average of USD 3.86 million per breach, and that compromised employee accounts were the most expensive root cause. Eighty percent of these incidents resulted in the exposure of customers’ personally identifiable information (PII), the costliest in the business.
The annual Cost of Data Breach Report is an in-depth analysis of real-world data breaches conducted by the Ponemon Institute and sponsored by IBM. The 2020 Cost of Data Breaches looked at data breaches experienced by over 500 organizations worldwide last year. The study is based on in-depth interviews with more than 3,200 security professionals in organizations that suffered a data breach over the past year.
As companies are increasingly accessing sensitive data via remote work and cloud-based business operations, the report sheds light on the financial losses that the organization can suffer if this data is compromised. A separate IBM study found that over half of employees new to working from home due to the pandemic have not been provided with new guidelines on how to handle customer PII, despite the changing risk models associated with the shift.
Some of the top findings from this year’s report include:
- Smart tech slashes breach costs in half: Companies who had fully deployed security automation technologies (which leverage AI, analytics and automated orchestration to identify and respond to security events) experienced less than half the data breach costs compared to those who didn’t have these tools deployed – USD 2.45 million vs. USD 6.03 million on average.
- Paying a premium for compromised credentials: In incidents where attackers accessed corporate networks through the use of stolen or compromised credentials, businesses saw nearly USD 1 million higher data breach costs compared to the global average – reaching USD 4.77 million per data breach. Exploiting third-party vulnerabilities was the second costliest root cause of malicious breaches (USD 4.5 million) for this group.
- Mega breach costs soar by the millions: Breaches wherein over 50 million records were compromised saw costs jump to USD 392 million from USD 388 million the previous year. Breaches where 40 to 50 million records were exposed cost companies USD 364 million on average, a cost increase of USD 19 million compared to the 2019 report.
- Nation-state attacks are the most damaging breaches: Data breaches believed to originate from nation-state attacks were the costliest, compared to other threat actors examined in the report. State-sponsored attacks averaged USD 4.43 million in data breach costs, surpassing both financially motivated cybercriminals and hacktivists.
“When it comes to businesses’ ability to mitigate the impact of a data breach, we’re beginning to see a clear advantage held by companies that have invested in automated technologies,” said Wendi Whitmore, Vice President, IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence. “At a time when businesses are expanding their digital footprint at an accelerated pace and security industry’s talent shortage persists, teams can be overwhelmed securing more devices, systems, and data. Security automation can help resolve this burden, not only enabling a faster breach response but a significantly more cost-efficient one as well.
Employee credentials and misconfigured clouds are attackers’ entry point of choice
Stolen or compromised credentials and cloud misconfigurations were the most common causes of a malicious breach for companies in the report, representing nearly 40% of malicious incidents. With over 8.5 billion records exposed in 2019, and attackers using previously exposed emails and passwords in one out of five breaches studied, businesses should rethink their security strategy via the adoption of a zero-trust approach – reexamining how they authenticate users and the extent of access users are granted.
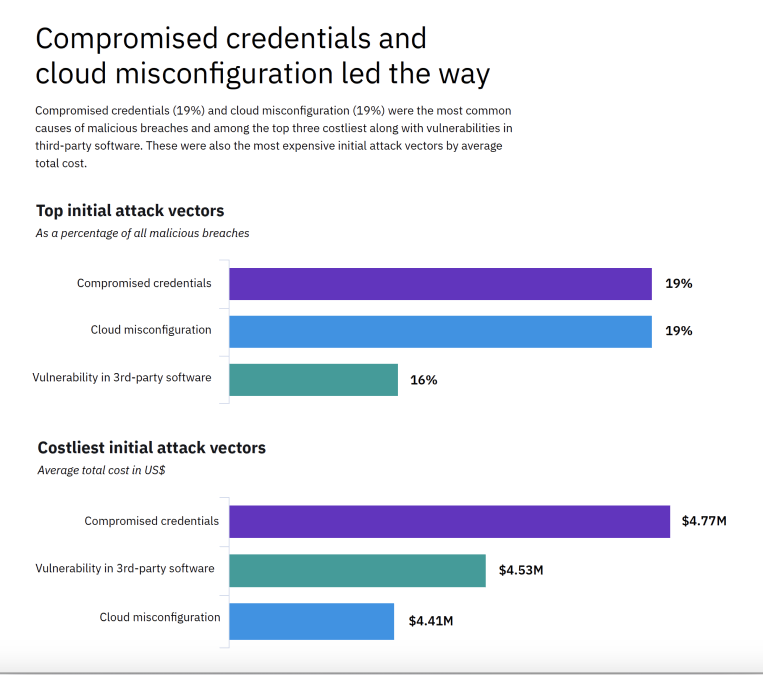
Similarly, companies’ struggle with security complexity – a top breach cost factor – is likely contributing to cloud misconfigurations becoming a growing security challenge. The 2020 report revealed that attackers used cloud misconfigurations to breach networks nearly 20% of the time, increasing breach costs by more than half a million dollars to USD 4.41 million on average – making it the third most expensive initial infection vector examined in the report.
State sponsored attacks strike heaviest
Despite representing just 13% of the malicious breaches studied, state-sponsored threat actors were the most damaging type of adversary according to the latest report, suggesting that financially motivated attacks (53%) don’t translate into higher financial losses for businesses. The highly tactical nature, longevity and stealth maneuvers of state-backed attacks, as well as the high value data targeted, often result in a more extensive compromise of victim environments, increasing breach costs to an average USD 4.43 million.
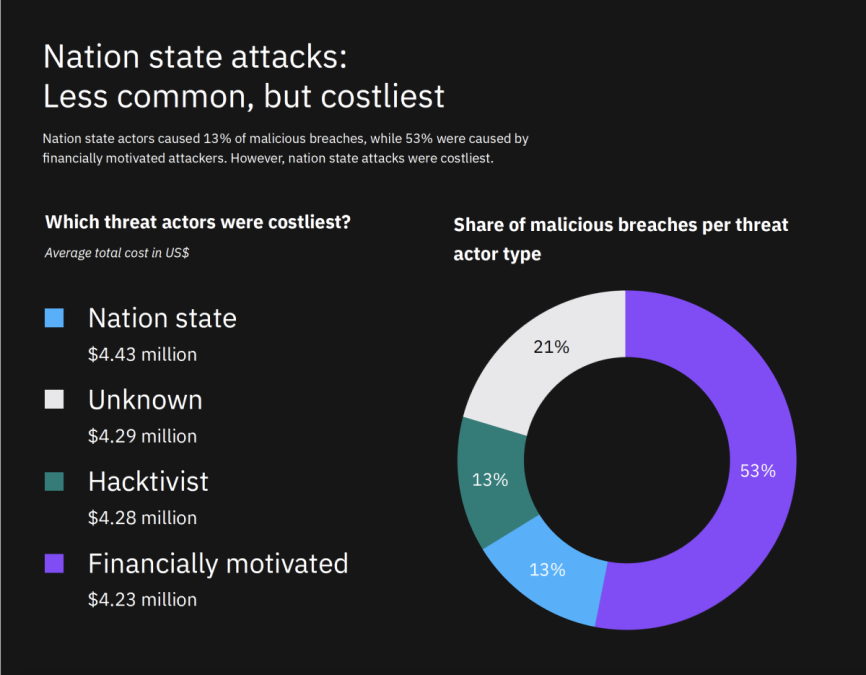
In fact, respondents in the Middle East, a region that historically experiences a higher proportion of state-sponsored attacks compared to other parts of the world, saw an over 9% yearly rise in their average breach cost, incurring the second-highest average breach cost (USD 6.52 million) amongst the 17 regions studied. Similarly, the energy sector, one of the most frequently targeted industries by nation-states, experienced a 14% increase in breach costs year over year, averaging USD 6.39 million.
Advanced security technologies prove smart for business
The report highlights the growing divide in breach costs between businesses implementing advanced security technologies and those lagging behind, revealing a cost-saving difference of USD 3.58 million for companies with fully deployed security automation versus those that have yet to deploy this type of technology. The cost gap has grown by USD 2 million, from a difference of USD 1.55 million in 2018.
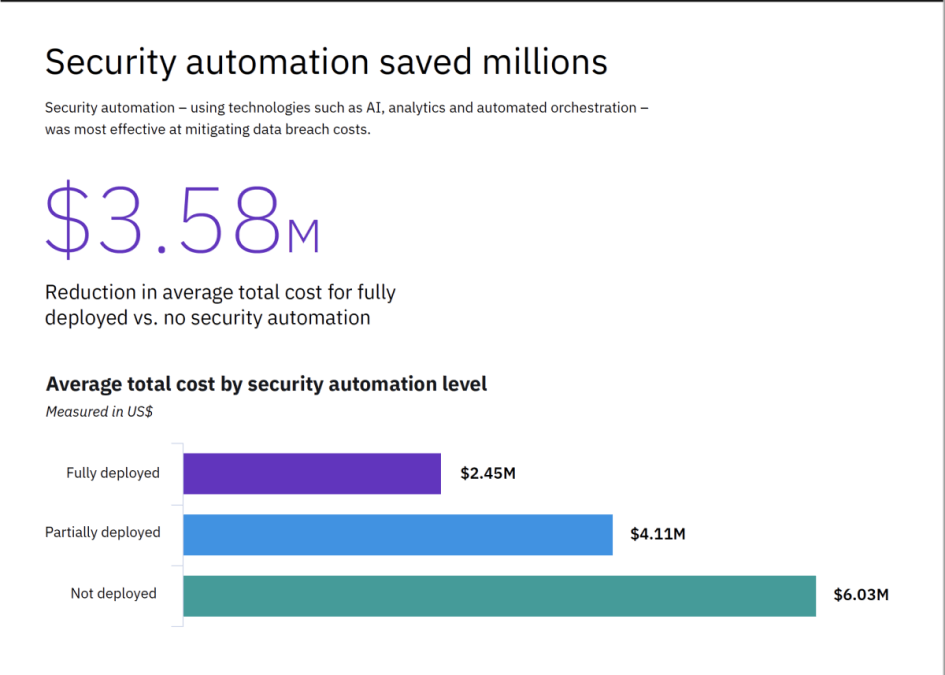
Companies in the study with fully deployed security automation also reported significantly shorter response time to breaches, another key factor shown to reduce breach costs in the analysis. The report found that AI, machine learning, analytics and other forms of security automation enabled companies to respond to breaches over 27% faster than companies that have yet to deploy security automation – the latter of which require on average 74 additional days to identify and contain a breach.
Incident response (IR) preparedness also continues to heavily influence the financial aftermath of a breach. According to the report, companies with neither an IR team nor testing of IR plans experience USD 5.29 million in average breach costs, whereas companies that have both an IR team and use tabletop exercises or simulations to test IR plans experience USD 2 million less in breach costs – reaffirming that preparedness and readiness yield a significant ROI in cybersecurity.
Additional findings
- Remote work risk will have a cost: With hybrid work models creating less controlled environments, the report found that 70% of companies studied that adopted telework amid the pandemic expect it will exacerbate data breach costs.
- CISOs faulted for breaches, despite limited decision-making power: Forty-six percent of respondents said the CISO/CSO is ultimately held responsible for the breach, despite only 27% stating their CISO/CSO is the security policy and technology decision-maker. The report found that appointing a CISO was associated with USD 145,000 cost savings versus the average cost of a breach.
- Majority of cyber insured businesses use claims for third-party fees: The report found that breaches at studied organizations with cyber insurance cost on average nearly USD 200,000 less than the global average of USD 3.86 million. In fact, of these organizations that used their cyber insurance, 51% applied it to cover third-party consulting fees and legal services, while 36% of organizations used it for victim restitution costs. Only 10% used claims to cover the cost of ransomware or extortion.
- Regional and industry insights: While the U.S. continued to experience the highest data breach costs in the world, at USD 8.64 million on average, the report found that Scandinavia experienced the biggest year over year increase in breach costs, observing a nearly 13% rise. Healthcare continued to incur the highest average breach costs at USD 7.13 million – an over 10% increase compared to the 2019 study.
To download and read the full report visit ibm.com/databreach
