In recent years, the world has witnessed several severe ransomware attacks. The Philippines has also experienced multiple ransomware incidents affecting organizations and businesses. The country’s national ICT department has reported over 50,000 cybersecurity threats in recent years, with affected organizations losing at least millions of dollars. These incidents have affected brand reputations and also served as a wake-up call for many businesses about the challenge of data protection.
Faced with an increasingly sophisticated and continuous wave of cyberattacks, many organizations have begun to recognize the importance of data security and proactively implement preventive measures. However, from an IT perspective, comprehensively protecting a large volume of data is not an easy task.
Maintaining data every day can become a burden, especially when businesses are operating systems that combine software and hardware from different vendors. In many cases, the system does not meet audit requirements, or the business finds it difficult to ensure the integrity and accuracy of the data.
In this context, a comprehensive backup appliance that integrates hardware and software is gradually becoming a viable option for businesses.
Redefining Backup Standards: Not Just Storage, but Also Recovery
So how can businesses choose a backup solution that ensures data is recovered correctly, completely, and quickly after an incident?
First, businesses need to ensure that source data can be backed up quickly, accurately, and completely restored. With devices using global deduplication technology, businesses can minimize backup time and bandwidth, thereby improving performance and achieving their Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
To further minimize the impact of ransomware attacks, businesses should consider a combination of on-site and off-site backups. These backups can be paired with immutable storage and WORM (Write Once, Read Many) technology, which ensures that data cannot be altered or deleted during the retention period. Additionally, off-site backups are encrypted before transmission to ensure secure data transfer to remote locations.
Beyond backup performance, verifying recovery capabilities is equally important. Businesses can create a sandbox environment within the device to test disaster recovery strategies without impacting the production environment. In addition, they can verify system backups by automatically creating videos to confirm data recoverability in the event of an incident. Individual systems, files, or recovery from physical to virtual (P2V) or virtual to virtual (V2V) can be performed based on the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) when attacked by ransomware.
Protecting Clean Data: A New Mindset in the Ransomware Era
Assuming that backup servers are immune to ransomware, encryption threats, or data breaches is not the way to go. Modern backup solutions’ robust security architecture focuses on three key areas:
- Role-based Access Control: This ensures precise control over who has access to data, guaranteeing that each user only has the permissions corresponding to their role in the organization.
- Blocking Unauthorized Access via IP: Limiting access to backup devices to only authorized IP addresses helps reduce the risk of unauthorized access or external attacks.
- Offline Backups: Isolating backup servers from the network when not in use. In addition to the 3-2-1 backup strategy (three copies, on two different media types, with one offsite), businesses can add an offline copy to ensure a clean backup that can be quickly restored in case of an incident.
Centralized Management, Enhancing Operational Efficiency
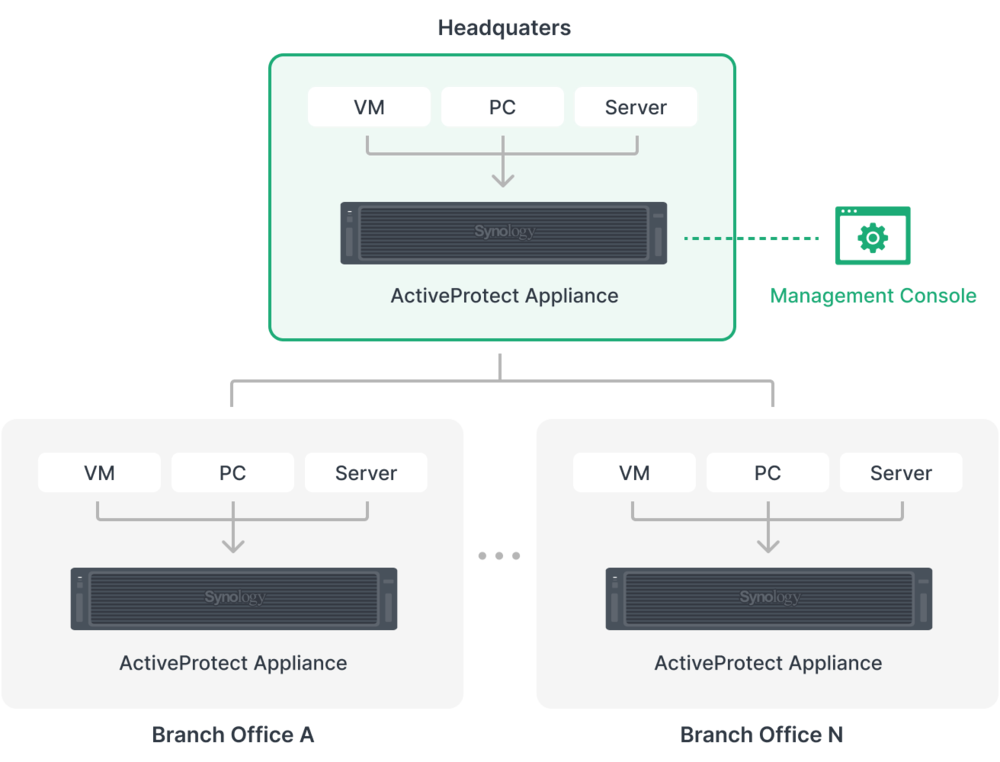
For businesses with multiple branches, managing decentralized backups often creates vulnerabilities. When an issue occurs at a branch, without an overarching view, IT teams may struggle to respond in a timely manner.
Some backup appliances today, such as ActiveProtect, support centralized management, allowing monitoring of up to 2,500 servers and 150,000 workloads from a single dashboard. This makes it easier to detect issues, check server status, and perform remote data recovery, helping businesses maintain continuous operations even in the event of a significant issue at any point.
Conclusion
Defending cybersecurity has never been about one single step. It requires building a comprehensive data protection strategy. Solutions like Synology’s ActiveProtect are helping organizations reduce manual workloads, standardize backup and recovery processes, save time, and ensure continuous operations.
With a strong security strategy and effective backup solutions, businesses can rest assured that their digital assets are protected, and operations can continue under any circumstance, especially when facing ransomware attacks.
