Over the past year, a concerning trend has persisted among the engineering and design sectors, in which the use of unlicensed software by large companies continues unabated.
Recent law enforcement actions across the region revealed that some of these companies are involved in the design and engineering of critical public infrastructure projects. This has prompted BSA | The Software Alliance to sound the alarm, emphasizing that using outdated and unsecured software in such projects may put public safety at risk.
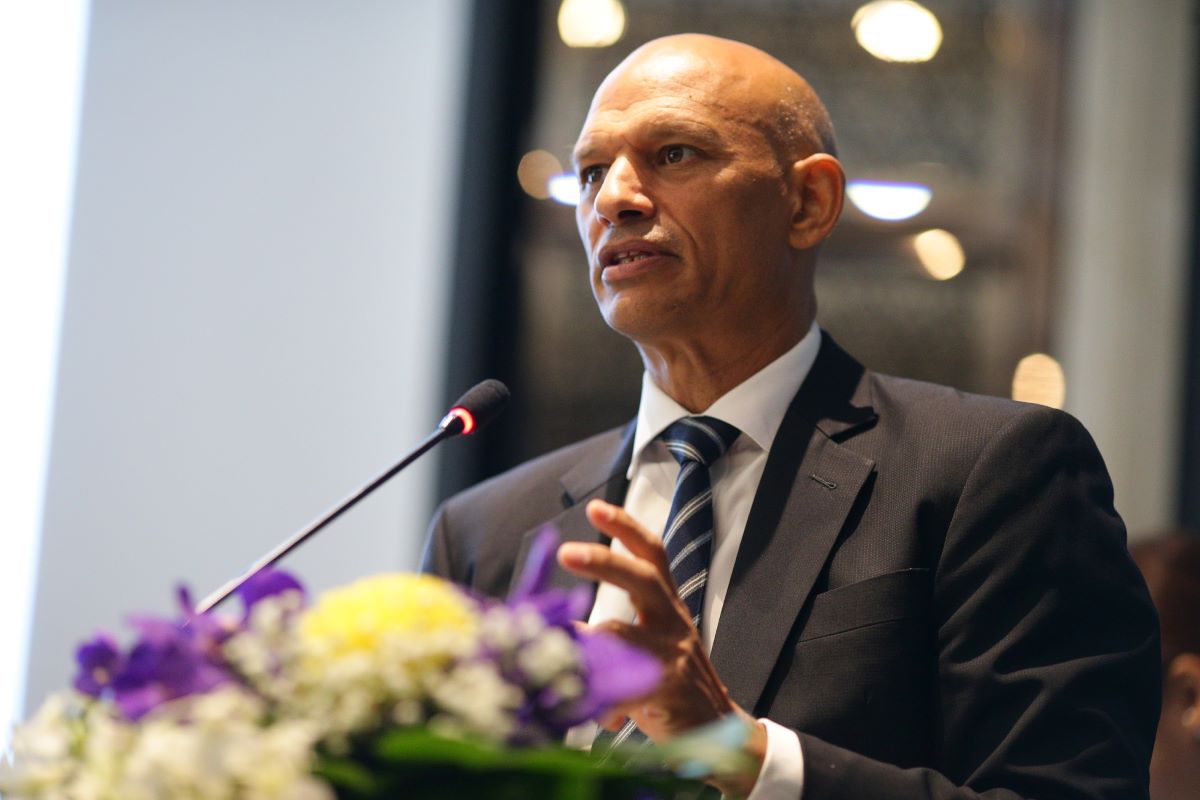

“Every CEO and business leader in the engineering and design industry should make it a New Year’s resolution to carefully manage their software assets,” said BSA senior director Tarun Sawney. “Governments across the region are looking closely at the software used in public works projects, ensuring that all taxpayer-funded infrastructure projects are designed using only safe, secure, licensed software.”
Unlicensed software is highly susceptible to malicious cyber threats, which are on the rise around the globe. In Southeast Asia, the cost of a data breach has reached an all-time high of more than USD3 million in 2023, marking a 6% year-on-year increase.
With the onset of the new year, it’s imperative for businesses, particularly those engaged in critical infrastructure projects, to adopt best practices aimed at combating the prevalent use of unlicensed software. In light of this, BSA has prepared a five-step plan to guide organizations in ensuring software compliance and boosting cybersecurity and safety.
1) Make licensed software your first line of defense against cybercrime
Using licensed software is not just a matter of compliance; it serves as the first line of defense against cybercrime for any organization. Licensed software providers regularly release updates to address newly discovered vulnerabilities, ensuring users are equipped with the latest security measures against potential threats.
Unlicensed software, on the other hand, creates a significant level of risk for organizations. These unauthorized programs are often missing essential security updates, meaning they introduce potential system vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals. The use of unlicensed software might expose engineering and design firms to malware, ransomware, and other threats that can compromise the integrity of their projects, expose their data, and disrupt their business operations.
Enforcing a zero-tolerance policy for unlicensed software is crucial for these organizations, as it requires every member to understand the risks associated with illegal software use. At the same time, business leaders must emphasize the role of licensed software in bolstering the organization’s cybersecurity defenses.
2) Buy software from legitimate and trusted vendors
Opting for reputable sources ensures that the software is not only genuine but also free from malicious added code or vulnerabilities that could compromise the security of an organization’s systems. Legitimate vendors adhere to industry standards, providing regular updates and support to enhance the software’s functionality and promptly address security issues.
Moreover, companies must aim to centralize their software procurement processes. By doing so, they can establish a standardized approach to vetting and acquiring software, reducing the risk of unintentional use of unauthorized or potentially harmful programs. This approach allows for better oversight, ensuring that all software adheres to company policies, licensing requirements, and security standards.
3) Develop a robust asset management system
One crucial aspect of effective asset management is conducting regular audits of software licenses. This involves maintaining accurate records and ensuring licenses are up to date. Failure to do so may result in legal consequences and financial penalties. This practice also helps to avoid under-licensing of software, which could lead to unintended violations and compromise the integrity of the organization’s cybersecurity framework. Unsupported software can create opportunities for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities.
Businesses should also realize that integrating AI in cybersecurity systems is now necessary. Since malicious actors are increasingly leveraging the technology to scheme sophisticated cyber attacks, businesses must keep pace with evolving threats by investing in AI-driven solutions. AI can play a pivotal role in analyzing emails and user behavior for potential threats, detecting suspicious sign-ins and user accounts, and enhancing authentication solutions. By embracing AI, organizations can fortify their defenses and proactively identify and counteract emerging cyber threats.
4) Build a culture of software compliance and cybersecurity
Raising awareness among team members is one of the crucial first steps to establishing a strong culture of software compliance and cybersecurity within an organization. Regular communication and educational sessions are essential to instill an understanding of the significance of compliance and the potential repercussions of lax cybersecurity. Businesses can invest in comprehensive training programs that cover the latest threats, compliance standards, and best practices to equip their workforce with the necessary knowledge to identify and mitigate risks. This foundational awareness can also cultivate a vigilant and proactive mindset among employees.
Moreover, fostering a collective commitment to cybersecurity is key. Actively involving team members in the organization’s cybersecurity efforts ensures a shared responsibility for maintaining a safe and secure digital environment.
5) Create practical policies that all employees can embrace
To maintain a strong compliance and cybersecurity culture, companies can adopt practical policies that promote employee participation. A key element of this approach involves establishing a clear and systematic process for reporting software non-compliance, threats, and vulnerabilities. Encouraging employees to actively identify and report potential security risks is pivotal in bolstering the organization’s defense against cyber threats. This also allows the company to swiftly respond to emerging issues and implement proactive measures to minimize the impact of cybersecurity breaches.
It may also be necessary to restrict access to certain software solely to employees who have undergone proper training. This serves as a preventive measure against potential system-wide damages resulting from errors made by untrained personnel. This approach mitigates the risk of inadvertent mistakes and underscores the importance of comprehensive training programs as an integral component of the organization’s cybersecurity strategy.
Using unlicensed software is against the law and may result in severe consequences, such as substantial fines and legal proceedings for violating intellectual property rights. Looking ahead to the new year, prioritizing software compliance becomes even more crucial, especially for companies involved in public works and infrastructure projects. Indeed, it is a fundamental step in ensuring the long-term security and safety of both individuals and organizations.